The output of the year’s total tonnage for the production of tungsten metal is very small compared to the basic metals. The latest estimates are: 60,000 to 65,000 metric tons primary tungsten metal (W) for the production – this corresponds to 75,000 to 83,000 metric tons of tungsten trioxide, WO3 (80% W). The allocation of this production would be more or less: 50,000 metric tons/year W from Chinese mines – nearly 80% of the world’s production 8,000 metric tons/year W from Western oriented national economies – approx. 13% 2,500 metric tons/year from other communist or CIS countries – approx. 7%
Worldwide consumption of tungsten metals
- A limited additional mining production outside China for a given time due to the decline of new projects, higher development and operation costs
- China has introduced an import tax on all primary products; the yearly tungsten export rate was reduced; many small mines had to be closed.
- The growth rate of economies like China and India has driven the demand of tungsten up to 10% p.a.
| Tungsten deposits | Tons W/a | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| China | 80,000 | 88 |
| Russia | 1,500 | 2 |
| Africa | 2,000 | 2 |
| Austria | 1,100 | 1 |
| Others | 7,500 | 7 |
| Total production: | 89,600 | 100 |
Da die Minenproduktion seit 2004 weitestgehend ruht, hat dies zu einem Defizit bei der Versorgung geführt. Dafür hat der Abverkauf von strategisch wichtigen Lagerhalden in den USA und Russland gesorgt. Diese sind entweder ausgeschöpft oder vollständig verwaltet. Japan hat seinen eigenen Lagerplatz seit 2008 erweitert.
Tungsten industry
- Primary tungsten producers – the mines that exploit and process in order to produce tungsten mineral concentrates.
- Secondary tungsten processing - processing plants that process the mineral concentrations to a series of tungsten powders including ammonium paratungstate (APT) being suitable for the downstream metal/production of alloys. These powders are often called “intermediate stages”.
- Tertiary tungsten producers – companies who produce finished tungsten metal, tungsten alloys, tungsten tools/extras, and other final tungsten products.
Tungsten products
The use of tungsten leads to the production of products of different categories in the industrial branch. The use of tungsten leads to the production of products of different categories in the industrial branch.
About 55% of the tungsten is used for the production of hard metals or cemented carbides; these are cutting, drilling, and wear materials being produced from tungsten carbide and cobalt and sometimes from small metals like titanium, tantalum, and niobium.


Approx. 20% of the tungsten is used to produce special steel alloys such as high-speed steel, heat resistant steel, and tool steel. These ones are mainly used in metal cutting applications and special application techniques.
About 17% of the tungsten is used to produce “milling products”; these products would include tungsten bolts, sheets, and wires/cables, electrical contacts, etc.


In addition, 8% of the tungsten is used in the chemical industry and for special applications.
Strategic importance of tungsten
A strategically important metal for China, the US, and Europe
It is essential for the industry, economic development, and national security where an insufficient supply in the country is missing.
Application areas where wear-free high-temperature settings increasingly occur
- High-performance manufacturing, cutting, and drilling tools
- Added steel for tensile strength and hardness, lamps and electronic devices
- aeroplanes, aerospace, and technology
- Mining, oil, gas, and construction industry
- Superalloys “ferro-tungsten”
- Military applications
- Nuclear installations
Positive outlook of tungsten
- China disposes on more than 60% of the worldwide reserves
- China only exports processed tungsten products
- China’s focus is on the national demand
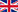
Tungsten APT (EU) 01.2018: 31,400 US $/MTU
Conclusions regarding tungsten
- Tungsten is a metal with unique features which make it one of the most important components in many industrial fields of application.
- Decisive features are a very high melting point, a very high density, hardness similar to a diamond, thermal and chemical stability, a very good conductivity, and environmental performance.
- Tungsten carbide is most importantly used in hard metals, which is mainly employed for industrial drilling and cutting tools. The second most important use is in electronic devices and special steels.
- 75% of the worldwide tungsten mine production is related to China; the supply in the Western world is highly limited.
- The US, Europe and Japan consume 31% of the mined tungsten worldwide, but only produce 3%.
- The national demand in China has increased and China has changed from a net exporter to a net importer of tungsten concentrates. The increased Chinese demand in combination with greater control of the Chinese government regarding their own tungsten industry and tungsten exports had the following results:
- The prices for tungsten have more than doubled since the beginning of 2010 to a current price of approx. 450 USD for APT (a tungsten intermediate product).
- There are concerns in regard to the supply reliability of tungsten concentrates to Western processors and industrial end users. This concern and other factors have resulted to a classification of tungsten as a “critical raw material” in the EU.
- The national consumption of tungsten in China has been predicted with a yearly growth of 8% between 2010 and 2013.
- Growth markets for tungsten are further identified, such as nickel-tungsten alloys which could replace chrome plating, and nickel-tungsten alloys which could replace gold-nickel coatings.
- The fields of application for tungsten in industry, aerospace and military are very important and tungsten is a strategically important raw material. There are stocks in the US and in Russia. China also indicated that they intend to build up stocks and there have been some discussions concerning the possible installation of European stocks.